Blog | Entrepreneurship, Personal Finance
Why Savers Are Losers
Contrary to popular belief, saving isn't going to get you where you want to go. Discover how to have your money work for you.
Rich Dad Personal Finance Team
October 03, 2024
Summary
-
Understanding the new rules of money and how it works is essential to your financial future
-
While many people think having a nest egg is secure, the truth is: savers are losers
-
The key to getting rich is to pay yourself first
Poor dad, Robert Kiyosaki’s natural father, believed in saving money. "A dollar saved is a dollar earned," he often said.
The problem was he didn't pay attention to changes in monetary policy. All his life he saved, not realizing that after 1971 his dollar was no longer money.
You see, in 1971 President Richard Nixon changed the rules of money. That year, the U.S. dollar ceased being money and became a currency. This was one of the most important changes in modern history, but few people understand why.
Prior to 1971, the U.S. dollar was real money linked to gold and silver, which is why the U.S. dollar was known as a silver certificate. After 1971, the U.S. dollar became a Federal Reserve Note -- an IOU from the U.S. government. Instead of our dollar being an asset, it was turned into a liability. Today, the U.S. is the largest debtor nation in history due in part to this change.
Taking a brief look back at the history of modern money, it's easy to understand why the 1971 change was so important.
After World War I, Germany's monetary system collapsed. While there were many reasons for this, one was because the German government was allowed to print money at will. The flood of money that resulted caused uncontrolled inflation. There were more marks, but they bought less and less. In 1913, a pair of shoes cost 13 marks. By 1923, that same pair of shoes was 32 trillion marks!


As inflation increased, the savings of the middle class was wiped out. With their savings gone, the middle class demanded new leadership. Adolf Hitler was elected Chancellor of Germany in 1933 and, as we know, World War II and the murder of millions of Jews followed.
A New System of Money
In the closing days of World War II, the Bretton Woods System was put in place to stabilize the world's currencies. This was a quasi-gold standard, which meant currencies were backed by gold. The system worked fine until the 1960s when the U.S. began importing Volkswagens from Germany and Toyotas from Japan. Suddenly the U.S. was importing more than it was exporting and gold was leaving our country.
In order to stop the loss of gold, President Nixon ended the Bretton Woods System in 1971 and the U.S. dollar replaced gold as the world's currency. Never in the history of the world had one nation's fiat currency been the world's money.
To better understand this, rich dad, Robert’s best friend’s dad and mentor, had him look up the following definitions in the dictionary.
"Fiat money: money (as paper money) not convertible into coin or species of equivalent value."
The words "not convertible into coin" were bothersome to Robert. So rich dad then had him look up the word: "fiat."
"Fiat: a command or act of will that creates something without or as if without further effort."
Robert asked, "Does this mean money can be created out of thin air?"
Nodding his head, rich dad said, "Germany did it and now we are doing it."
"That's why savers are losers," he added. "I fought in France during World War II. That's why I never forget that it was after the middle class lost their savings that Hitler came to power. People do irrational things when they lose their money."
Most economists would disagree with rich dad's correlation between the loss of savings and Hitler. It may not be an accurate lesson, but it’s an unforgettable one.
Between 2000 and 2005 housing prices went through the roof. Oil went from $10 a barrel in 1997 to over $60 a barrel in 2005. Gold went from $275 an ounce in 1996 to over $475 an ounce in 2005.
In spite of all these increases in prices, the federal government's economists say, "Inflation is low. It's under control." They are allowed to say that because the government is charged with only monitoring inflation in consumer prices -- not asset prices. The consumer price index (CPI) is the pressure gauge the government watches because they want to make sure the consumer is happy finding bargains at Wal-Mart, which is easy because China is forcing consumer prices down.
The problem is our dollars return to the U.S. to buy our assets. In simple terms, we send cash overseas to buy goods, and overseas investors take our cash and use it to buy our assets. That's why the Wal-Mart shoppers find bargains in the store but can't afford to buy a house, gas, gold, or stocks. Those same "consumers" also worry about their jobs going overseas.
In summary, investors shop for asset bargains, and consumers shop for consumer bargains and try hard to save money that is not really money. That is another reason why the rich are getting richer.


Where to start
So where do you begin?
It all starts by thinking differently. Let’s say you’re only getting 1% interest on your savings; start thinking: “Where can I get a better return on my money?” And if you don’t know, go learn. Go study. Go figure it out because there are plenty of places out there where you can get a better return on your money.
You don’t have to go out and buy a ten-unit apartment building or throw all of your money in the stock market. But, you have to do something! Learn about other options… just get started; do anything but rely on savings. Remember, savers are losers.
Pay yourself first
Later in life, when Robert and his wife, Kim were broke, they concluded that in order to realize their dreams, they had to pay themselves first, then pay their creditors.
In came the 10/10/10 plan. Each month, whether it made sense or not, they put aside a sum of money into their asset column, and treated it just like an expense.
They took 30% of their paychecks and divvied it three ways:
-
10% Investments
-
10% Charity or tithing
-
10% Savings
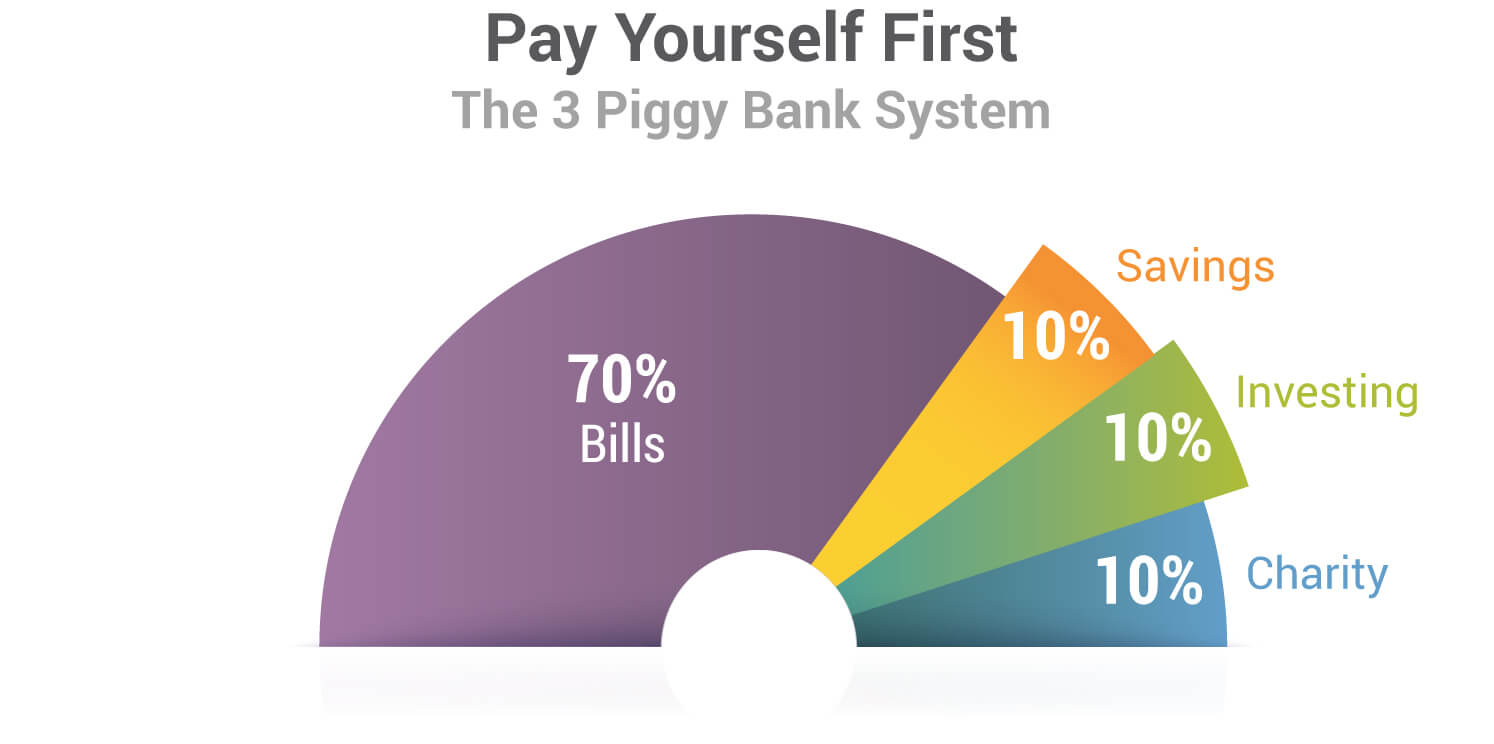
Now, while they did save a small amount for emergencies and special opportunities, they did not rely on our savings whatsoever to become wealthy. Meanwhile, their investments were consistently making money in the background.
Savers are losers
As Burt Dohmen of Dohmen Capital Research, says, “You don’t want to be on the side of the losers!”
With this in mind, let’s say you want to stop being a saver, and instead, have your money work for you.
Start by seeking advice from people who practice what they preach and are successful. Don’t turn to your financial planners for education. You’ll probably get a sales pitch! Instead, get your own financial education.


The most effective way to get going is by learning and taking action. Whether it’s $100 or $1,000, you’ve got to put some money in the game and get started. When Robert began investing, he started with one-ounce silver coins.
It doesn’t matter how much money you have, what matters is what you do with it and how you control it.
Original publish date:
October 18, 2012